Overview
This protocol details the method for determining the initiation age (ai) and C+D period in bacterial cells, as well as the calculation of the C and D periods, the generation of a theoretical DNA histogram, and the calculation of the average number of replication forks.
Determination of initiation age (ai) and C+D:
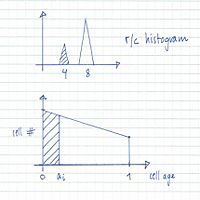
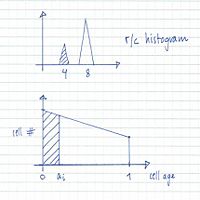
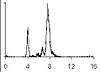
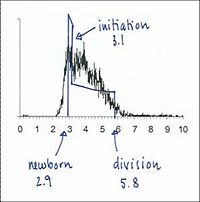
From flow cytometry analysis of cells treated with rifampicin and cephalexin (run-out histogram) the proportions of cells that had not initiated replication at the time of drug action (4-origin-cells, streaked) and cells that had initiated (8-origin-cells) can be estimated.The initiation age (ai) can be found from the theoretical age distribution described by this formula,
[math]\displaystyle{ F=2-2^{\frac{(\tau-a_i)}{\tau}} }[/math]
where F is the fraction of cells that had not initiated and τ is the generation time, or from the estimated graph of the theoretical age distribution (streaked portion).
This gives:
[math]\displaystyle{ a_i=\tau-\frac{log(2-F)}{log2}*\tau }[/math]
which is the same as this (log2 is 1):
[math]\displaystyle{ a_i=\tau-log(2-F)*\tau }[/math]
If you have for example a generation time τ=84 minutes and the portion of cells with 4 origins is 66% the formula gives:
[math]\displaystyle{ a_i=84-log(2-0.66)*84=48.5 }[/math]
The C+D period is estimated from the initiation age (ai), the generation time (τ) and the number of generations spanned per cell cycle.
Example:
4-origin-cells: 23 %
Generation time (τ): 27 min
Initiation age (ai): 5 min
Determination of the C and D periods:
The C period is found from the oriC/terC ratio obtained by Southern blot or qPCR analysis (oriC/ter ratio determination) and the generation time (τ):
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{oriC}{terC}=2^{\frac{C}{\tau}} }[/math]
which gives:
[math]\displaystyle{ C=log_2(\frac{oriC}{terC})*{\tau} }[/math]
The D period is found from the C+D and C period:
[math]\displaystyle{ D = (C+D) – C }[/math]
Example (continues):
C period calculated from the oriC/terC ratio: 49 min
D period = (C+D) – C
D period = 76 min – 49 min = 27 min
The theoretical exponential DNA histogram:
A theoretical exponential DNA histogram can be drawn to check whether the obtained values fit with the experimental data. From the C+D period the DNA content of the cells at different time points in the cell cycle can be calculated.
Example:
The individual values of C and D can be varied
to obtain a shape of the theoretical histogram
that gives the best fit to the experimental histogram.
Calculation of the average number of replication forks when D=τ:
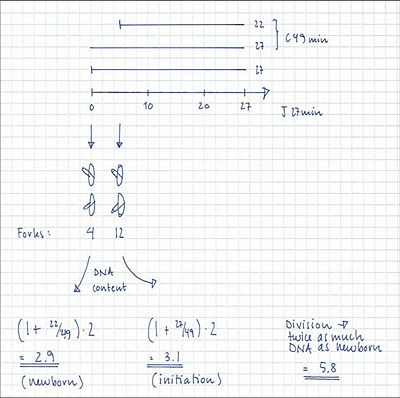
In the example given above, 23% of the cells contain 4 replication forks (4-origin peak in run-out histogram) and 77% contain 12 replication forks (8-origin peak), hence the average number of replication forks in the cell population will be:
(4 x 0.23) + (12 x 0.77) = 10.2 forks
Calculation of the average number of replication forks when D≠τ:
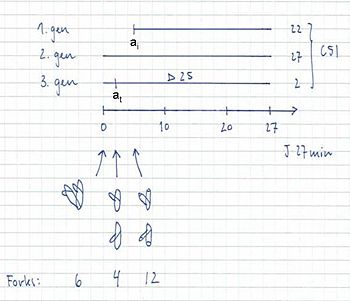
Example:
4-origin-cells: 23%
8-origin-cells: 77%
τ = 27 min
ai = 5 min
C = 51 min
D = 25 min
C+D = 76 min
- 12 forks → 8-origin peak in run-out histogram = 77% of the cells
- 6 and 4 forks → 4-origin peak in run-out histogram = 23% of the cells
- The fraction of cells containing 6 forks: F = 2 – 2((τ-at)/τ) = 2 – 2((27-2)/27) = 0.10
- The fraction of cells containing 4 forks: 0.23 – 0.10 = 0.13
- The average number of replication forks: (6 x 0.10) + (4 x 0.13) + (12 x 0.77) = 10.4 forks