Overview
RNA extraction with TRIzol (Invitrogen product name) or the equivalent TRI (Sigma-Aldrich product name) is a common method of total RNA extraction from cells based on the research of Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. 1987 [1] and reviewed by the authors again in 2006 [2]. It takes slightly longer than column-based methods like RNAeasy b
ut it has higher capacity and can yield more RNA. Along with chaotropic lysis buffers it is generally considered the method that gives the best quality RNA.
Principle
- guanidinium isothiocyanate (powerful protein denaturant) -> inactivation of RNases
- acidic phenol/chloroform -> partitioning of RNA into aqueous supernatant for separation
Note: low pH is crucial since at neutral pH DNA not RNA partitions into the aqueous phase. Check the pH of old TRIZOL/TRI reagents!
Reagents
- TRIzol or TRI reagent
- If you want to make your own reagents, see here
RNA extraction using self-made guanidinium-acid-phenol reagents
- 0.8 M sodium citrate / 1.2 M NaCl
- isopropanol (2-propanol)
- chloroform
- 75% EtOH in DEPC H2O
- RNase free water (filtered or DEPC)
Steps
cell lysis
 Cell lysis only takes a few minutes per well, but tissue homogenisation can take 10-20 minutes per sample depending on how tough the tissue is.
Cell lysis only takes a few minutes per well, but tissue homogenisation can take 10-20 minutes per sample depending on how tough the tissue is.
- (PBS wash)
- add trizol (cell lysis)
- 1ml / 3.5 cm diameter well (6-well)
- 5ml / 75 ml bottle
- homogenise by pipetting several times (mechanic lysis)
- alternative for tubes: vortex 1 min
- alternative for tissue: grind 1 g tissue in liquid nitrogen in a motar and pestle, put tissue into plastic screw-cap centrifuge tube + 15 ml TRIzol reagent, incubate samples for 5 min at room temp or 60° C (scaled up as needed)
- (5min at RT for complete dissociation of nucleoprotein complexes)
 RNA is stable in trizol which deactivates RNases. You can take a break at this point keeping the sample in trizol for a short time or freezing it for a longer one.
RNA is stable in trizol which deactivates RNases. You can take a break at this point keeping the sample in trizol for a short time or freezing it for a longer one.
phase separation
 15-45 min depending on number of samples and whether an additional chloroform wash is necessary
15-45 min depending on number of samples and whether an additional chloroform wash is necessary
- add chloroform (1/5 volume of trizol; e.g. 0.2ml to 1ml)
- shake for 15 sec (Eccles protocol: do not vortex)
- incubate 2-5 min at RT
- spin max. 12000g, 5-15 min, 2-8°C
- if centrifugation hasn’t been sufficient the DNA-containing interphase will be cloud-like and poorly compacted
 If supernatant appears turbid an additional chloroform cleaning step can be inserted here.
If supernatant appears turbid an additional chloroform cleaning step can be inserted here.
- transfer aqueous upper phase into new tube
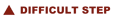 Take care not to aspirate the DNA-containing white interface. This quickly happens and will lead to DNA contamination in your RNA prep.
Take care not to aspirate the DNA-containing white interface. This quickly happens and will lead to DNA contamination in your RNA prep.
TRIZOL phases after chloroform addition TOP - colourless aqueous phase (RNA) - 60% TRIZOL volume MIDDLE - interphase (DNA) BOTTOM - red (organic) phenol-chloroform phase (proteins & lipids)
RNA precipitation and wash
 20-40 min depending on number of samples
20-40 min depending on number of samples
- add isopropanol (70% of aqueous phase or 1/2 trizol volume)
- 0.8 M sodium citrate or 1.2 M NaCl can be added
- (incubate 10min at RT)
- spin max g, 10-15 min, 4ºC
- remove supernatant
- (alternative RNA precipitation – RNeasy from Qiagen) better than alcohol precipitation for smaller amounts of RNA (less risk of losing a miniscule nucleic acid pellet); also reduces risk of organic solvent contamination
similar kits to RNeasy: MinElute kit, or Affymetrix sample clean-up
RNA wash
 15-30 min depending on number of samples
15-30 min depending on number of samples
- wash pellet 70% EtOH (add & vortex briefly)
- 70% ethanol prepared with RNase-free water
 some prefer to wash the pellot more than once with 70% ethanol
some prefer to wash the pellot more than once with 70% ethanol
- spin max g, 2-10 min, 4ºC
- air-dry pellet for 5-10 min
 Do not overdry the pellet or you won’t be able to redissolve it.
Do not overdry the pellet or you won’t be able to redissolve it.
 optional add RNase inhibitor
optional add RNase inhibitor
 incubate at 55-60 C° for 10 min if hard to redissolve
incubate at 55-60 C° for 10 min if hard to redissolve
- transfer to eppendorf tube
- spin 4° C, 5 min (to pellet undissolved material)
redissolving of RNA
- dissolve pellet in 50-100 µl filtered or DEPC H2O (note: DEPC inhibits RT reaction)
- alternatively, 0.5% SDS
pipetting up and down, heat to 55-60°C for 10 min
Common mistakes
- use too little trizol; very small volumes are hard to separate and will most likely lead to contamination
- aspirate some white interphase (DNA) when removing aqueous supernatant (RNA)
- use phenol/chloroform of the wrong pH (has to be acidic)
- not working under the hood (phenol is toxic , chloroform is a narcotic )


